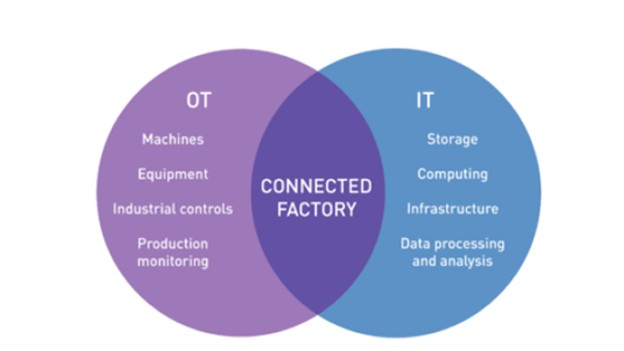
Manufacturing is a huge industry in Malaysia. It deals with both the fields; IT and OT. IT is basically all about digital information, network storage, cloud computing, and data-related hardware and software.
Whereas OT encompasses the systems that keep a check on the operations of physical equipment such as machines, devices, plants, and pumps. Both fields need to work together in order to bring laurels to the manufacturing industry in Malaysia.
However, due to risks regarding cybersecurity and a couple of other reasons, it is quite hard to bring both groups on the same page. Nonetheless, there is a need to bridge the gap so that IT and OT come together to create a full-fledged smart manufacturing industry.
The aspect of cybersecurity in IT and OT is essential because Malaysia has been flourishing really fast in the digital world. Due to the rapid popularity of digitalization in Malaysia, the risks of cybersecurity are also maximizing thereby. Hence, the convergence of IT and OT in manufacturing come across the challenge of cybersecurity at the forefront.
So, in this article, we will try to find out how to bridge the gap between IT and OT in manufacturing while dealing with the risks of cybersecurity in Malaysia.
Without any further ado, let’s delve in!
Role of IT and OT in Manufacturing and the Risks of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity has been a priority for Malaysians across all the major sectors, emphasizing a lot on the manufacturing industry. In order to understand the interest of the government of Malaysia in cybersecurity, you can assume from their allocation of US$434 million to prepare for the upcoming challenges posed by cyber-attackers to strengthen the country’s cybersecurity.
Malaysia Cyber Security Strategy (MCSS) launched the program for the years 2020-2024.
Understanding IT in Manufacturing
- What is IT?
IT in manufacturing is about transactional processes and includes a data management component, for example, a database. So, the data that is included in such storage and retrieval activities are mainly based on IT.
Deploying an IT Infrastructure in Manufacturing Industry
Basically, IT infrastructure falls into 3 major categories; system infrastructure, network infrastructure, and storage infrastructure.
- System Infrastructure:
System infrastructure deals with a wide variety of critical actions. It encompasses the management of all the IT assets within the data centers. For all such tasks, a chief technical officer (CTO) is in-charge.
- Network Infrastructure:
Network infrastructure makes sure that the configuration of all the linked networks is working fine and all the applications are having continuous access to the resources, ensuring that the network is safe.
- Storage Infrastructure
Lastly, storage infrastructure is responsible for keeping safe all the important assets of the manufacturing industry.
In order to broaden the study of the IT infrastructure in the manufacturing industry, the categories are further divided into 5 main components. So, let’s discuss them NOW:
- Computer Hardware Platforms
All the tangible components of the infrastructure like computers, servers, cybersecurity tools, boosters, routers, repeaters, wires, supplies, or cooling units make up the computer hardware that ensures the use of the IT environment.
- Operating Systems Platform
This is the platform that deals with the interface of hardware with software, middleware, and the application layers of the IT infrastructure. Operating systems are the main components that enable the users to operate the hardware.
- Software Applications
The IT infrastructure mostly consists of physical components but it might extend to a few software applications as well. It consists of both enterprise-level software like Oracle, SAP, or Microsoft and client-level applications that take advantage of the enterprise layer. A number of layers of software combine in order to make the hardware intelligent, thereby performing actions like calculation, interaction, and even cognizance.
- Data Management and Storage
Data management and storage act as the main areas in the IT infrastructure. It basically deals with the storage of data and performs the actions like an oversight. Moreover, it handles the physical components as well like data servers. Plus, it handles software components like database management systems that are used to organize databases.
- Networking And Telecommunications
The networking and telecommunications of a manufacturing industry come under the domain of IT infrastructure. It deals with everything from virtual network software to modems, routers, or wires. Plus, it also includes the infrastructure linked with internal and external servers that are responsible for hosting cloud-oriented applications and websites.
Understanding OT in Manufacturing
- What is OT?
OT is a group of computing systems that deal with managing, monitoring, and controlling the physical objectives of the operations in the manufacturing domain. Several OT activities include controlling the environment settings, keeping a check on infrastructures, or assigning tasks to the robots available on the manufacturing floor. OT is commonly used in the manufacturing industries.
Talking about OT data, it encompasses the raw data received from sensors, devices, and tools for further processing. The OT data provides information regarding controlling the processes within manufacturing workflows. This information is processed further to take help in decision-making.
How to Set an OT Infrastructure in Manufacturing?
OT systems are the core of OT/IT solutions that manufacturers require to promote production effectiveness to reach the targeted revenue. The cybersecurity challenges disrupt the IT/OT convergence. Hence, there is a need to plan and build the OT infrastructure in such a way that the environment remains secure.
Down below is the personalized 8-step approach to planning your OT infrastructure for manufacturing:
Step 1:
Develop policies that are matching to the OT environment of your manufacturing organization.
Step 2:
Identify the level of complexity in the OT environment through the following ways:
- Keeping a check on the production process.
- Monitoring and supervising the production process while lending automatic control.
- Managing the workflow in order to obtain the desired results while maintaining the records and optimizing the production process.
Step 3:
Have a look at the IT and OT convergence points. Every floor in the manufacturing industry comprises an overlapping branch. Hence, it is essential to identify that particular branch to chart them accurately.
Step 4:
OT will help you to identify a huge amount of data when connected to the tools that are capable of drawing these inferences. Hence, the OT/IT convergence should be made easier for the final data parsing manufacturing tools and devices.
Step 5:
In this step, the workflows must be established in order to maintain change management, obsolescence management, and disaster management. The OT asset management is responsible for compliance with the laid standards and protocols.
Step 6:
In step 6, training and workforce development are critical to equip the necessary skills in the workers in order to manage the OT environment. Training is very much needed so that security is ensured and workflow is never hindered. The training must take place in a modern, fully-equipped arena for better learning.
Step 7:
Setting up and maintaining the OT environment is another effort that ensures smooth operations within the manufacturing industry.
Step 8:
OT infrastructure requires help and assistance from leaders that have already worked really well in their personal space. Business leadership is always critical and therefore, the results are actually seen in the outcomes.
Why Cybersecurity Is Essential in OT and IT?
As cybersecurity’s need is increasing in every other department, OT and IT also require a completely safe environment in order to maintain the operations of the manufacturing industry. The task of solidifying devices, protocols, systems, networks, and users is now mandatory as no one is willing to share their private information.
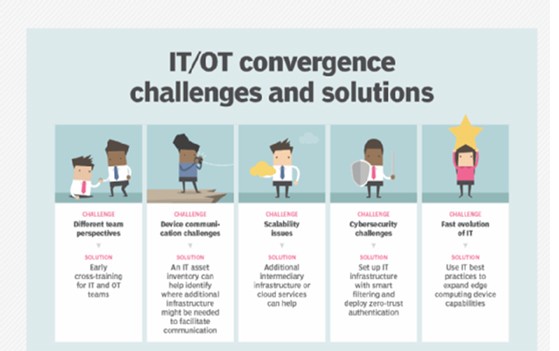
Cybersecurity has long been an issue in the IT and OT fields. In order to make sure that the users safely connect to the devices and networks, the main aim should be to anticipate such cyber-attacks.
Protecting the systems and networks becomes even more difficult when these get more and more connected.
Hence, new vulnerabilities are witnessed that are easily exploited by cyber-criminals in order to gain unauthorized access to networks. In Malaysia, more than 90% of the manufacturing organizations that operate IT/OT systems have come across one or more cyber-attacks in a single year, according to the Ponemon Institute of Research.
Apart from that, around 50% of the organizations faced OT infrastructure cyber-attacks that made the system go down entirely, disrupting the flow of information. The World Economic Forum highlighted that IT/OT cyber-attacks have been extremely critical and are ranked among the top 5 of the gravest cybersecurity risks. This is quite alarming!
The Bottom Line
As coming towards the end of the article, the concerns of cybersecurity are quite evident in IT/OT environments within the manufacturing industry in Malaysia and all over the world. But the main task is to make the system so strong that no power is able to break down the system in any case.
Otherwise, the main agenda should be to anticipate minor or major cyber-attacks so that an action could be taken beforehand in order to save the organizations from further damages. For it, the government of Malaysia is working really hard!